What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic Retinopathy is an eye condition that occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
There are two main types of Diabetic Retinopathy:
1. Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR):
In NPDR, the blood vessels in the retina become weak and start to leak, causing swelling and damage to the retina.
2. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR):
This more serious stage happens when blocked blood vessels lead to the growth of new, abnormal vessels. These fragile vessels can bleed easily, leading to internal bleeding, scar tissue, and retinal detachment — all of which can cause significant vision loss.
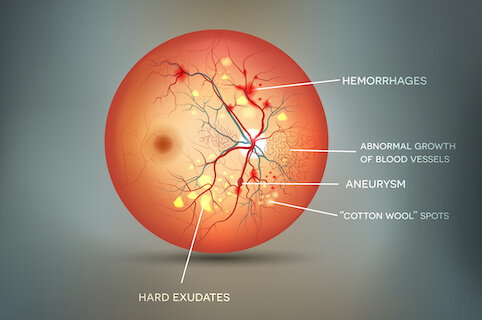
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Blurred or distorted vision
Dark spots or floaters in your field of vision
Fluctuating vision (vision getting better or worse over time)
Difficulty seeing at night
Sudden vision loss (in advanced stages)
Empty or dark areas in your vision
Who Is at Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy?
People with Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes
Longer duration of diabetes — the longer you’ve had diabetes, the higher the risk
Poor blood sugar control
High blood pressure (hypertension)
High cholesterol levels
Pregnant women with diabetes
Smokers
Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy
Control Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar is the first step. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and diabetes medications (like insulin or oral tablets) help slow disease progression.
2. Laser Therapy (Photocoagulation)
A laser is used to seal leaking blood vessels and prevent new abnormal vessels from forming. This protects the retina and helps slow vision loss.
3. Anti-VEGF Injections
Anti-VEGF medications block a protein that causes abnormal blood vessel growth and leakage, reducing swelling and improving vision.
4. Vitrectomy
In advanced cases, surgery may be needed to remove the vitreous gel from the eye. This gives better access to the retina and helps treat bleeding or retinal detachment.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Drugs like corticosteroids and NSAIDs help reduce inflammation and protect the eye from further damage.
6. Intravitreal Implants
Tiny steroid-releasing implants (like dexamethasone) are placed in the eye to reduce swelling and improve vision over time. These do not need to be removed.
FAQs – Diabetic Retinopathy American Laser Eye Hospitals
Diabetic Retinopathy is an eye condition caused by high blood sugar levels damaging the tiny blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to vision loss if untreated.
Anyone with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes is at risk, especially if they have poor blood sugar control, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or have had diabetes for many years.
Early stages may show no symptoms. As it progresses, symptoms may include blurred vision, floaters, dark spots, trouble seeing at night, and sudden vision loss.
Yes. Treatments include blood sugar control, laser therapy (photocoagulation), anti-VEGF injections, vitrectomy surgery, and intravitreal steroid implants depending on the stage of the disease.
We offer state-of-the-art diagnostic technology, expert retina specialists, personalized treatment plans, and advanced procedures like laser therapy and vitrectomy – all under one roof.
